# Create a Database Index
By creating indices for Core Engine modules, you can speed up data retrieval from the database. A database index will be loaded into RAM and retrieved immediately.
We recommended creating an index for custom fields and large amounts of data to improve the performance of the system during searches.
Index Editability
After creating a new index, you can edit it until the next system reload or restart. After that an index is active in the database and can no longer be adjusted or deleted.
Default indices are therefore non-editable.
# Index Configuration
An index is stored in its module's folder: modules/{module_name}/index/{index_name}.4apdbindex.
For index creation, use a module's admin snap-in or create it directly in XML (examples).
MySQL and SQL Server
Depending on whether you use MySQL or SQL Server, there are different conditions to consider. Please note our conditions and requirements for creating an index here.
# Database Index Admin Snap-in
To create a database index in the administration area, go to admin snap-in Module configurations/{module_name}/Database index:
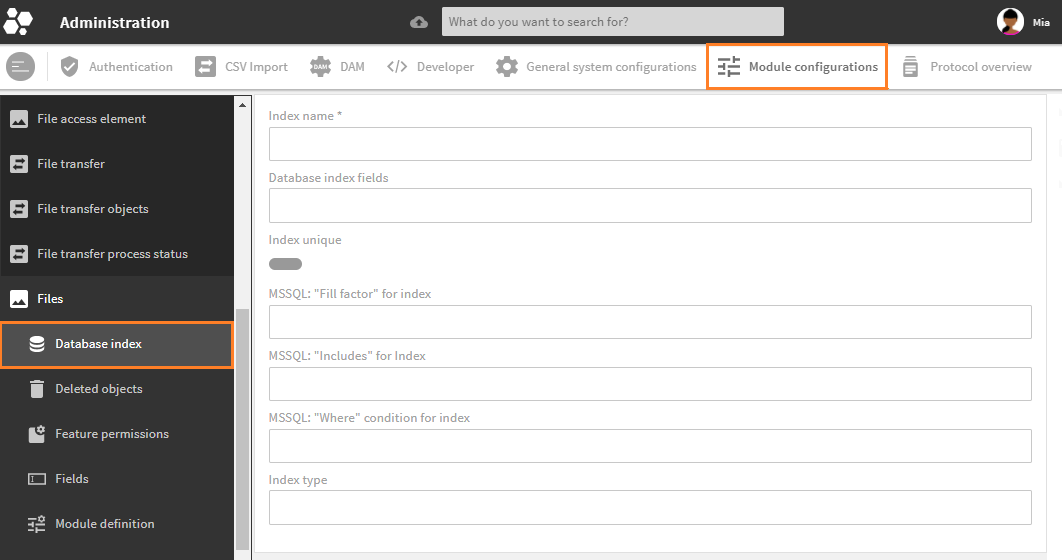
Create view in module Files
| Field | XML | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Index name | Unique file name for this index, will be complemented by .4apdbindex.No upper cases, spaces, or special characters allowed, only underscore. | |
| Database index fields | fields | Assign one or more database fields to the index. Only name is required, attributes order (supported only by SQL Server) and length (supported only by MySQL) are optional. (How to set field attributes) |
| Index unique | unique | If set to true, a unique index is created for native database fields. A unique index ensures the index key columns do not contain any duplicate values. |
| SQL Server: "Fill factor" for index | fillfactor | SQL Server only. Use to adjust and set a percentage fill factor value ranging from 1 to 100 (default database value: 100). Entry is optional. |
| SQL Server: "Includes" for Index | include | SQL Server only. Entered database fields are set to INCLUDE (included in the index as non-indexed fields).If using MySQL, these fields are added to a non-unique index, and ignored for a unique index. |
| SQL Server: "Where" condition for index | where | SQL Server only. Sets the search condition WHERE to limit the index, e.g. deleted=0. |
| Index type | type | MySQL only. Index type which is created. Currently, only binarytree is supported and automatically set. Ignored if using SQL Server. |
Please note: Toolbox actions "Edit" and "Delete" for whole indices, or their specifications (e.g. their assigned fields) will only take effect for new indices before a reload. After that, these actions will have no effect on the actual index in the database.
# Field Attribute Notation
The admin snap-in does not support complex data types. In the snap-in, the length and order attributes for the fields element must therefore be entered in the following notation:
fieldname(20)fieldname(10) ascfieldname desc
# XML Example for MySQL
<db_index>
<fields>
<field order="desc" length="123">name</field>
<include>
<field>name</field>
</include>
</fields>
<unique>false</unique>
<type>binarytree</type>
</db_index>
# XML Example for SQL Server
<db_index>
<fields>
<field order="desc" length="123">name</field>
</fields>
<unique>false</unique>
<fillfactor>80</fillfactor> <!-- 0 - 100 -->
<where>deleted = 'true'</where>
<include>
<field>name</field>
</include>
</db_index>
# Conditions and Limitations for Creating an Index
Indices over multiple fields are only allowed if all fields from elements
fieldsandincludeare in the module table. This means:- all fields must be native
- there must be no lists, dimensions, or special fields such as metrics or CEObjectLink.
Currently, no index can be created on fields with dimensions.
Applies for MySQL only:
orderattribute from elementfieldwill be ignored (only supported from version 8.0)typewill be set tobinarytreeautomaticallyfillfactorwill be ignored- Fields from
includeare included in the index only if the index is not unique. If the index is unique, these fields are ignored.
Applies for SQL Server only:
lengthattribute from elementfieldwill be ignoredtypewill be ignoredfillfactormay be set (blank or 1 to 100)wherecan be added as a condition- Fields from
includeare included in the index as non-indexed fields. - No index can be created on
CEText. An index on nvarchar(max), varchar(max), etc., is not allowed.
# Indices for Fields That Are Not Created in the Module Table
Data types for index on field value |
|---|
|
Data types for index on field normalized |
|---|
|
Data types for index on fields link_module, value |
|---|
|
Please note: The Core Engine automatically creates an index for link_module, value. No further index can be created.